The Soldier Health Monitoring and Position Tracking System allows the military personnel to track the current GPS position of a soldier and also checks the health status by detecting heartbeat of a soldier in realtime.
Soldiers Health Monitoring and GPS Tracking System
Introduction
Modern warfare demands real-time solutions for soldier safety. Soldiers risk injury and getting lost during missions. Delayed medical attention or search efforts can be deadly and can jeopardize national security. This project proposes a soldier health and location tracking system. Sensors monitor vitals (heart rate, temperature) and location (GPS). Wireless communication transmits data to a Blynk application accessed on the PC. This unit tracks soldier location and health, triggering alerts for abnormal readings. This system can significantly improve soldier safety by ensuring faster medical response for injured personnel and reducing search times for lost soldiers. However, further considerations include data security, low-power sensor technology, and system scalability for large-scale deployment.
Overview
The Smart Soldier Gear project, integrated with VSD Squadron technology, enhances soldier safety and operational efficiency through advanced wearable systems. The gear includes a pulse sensor (RC-A-4015) to monitor vital health parameters continuously. Any deviations from predefined thresholds trigger emergency alerts. A GPS module tracks the soldier’s real-time location. Data from these sensors are processed by a microcontroller and transmitted wirelessly via the HC12 RF transceiver directly to the Blynk cloud using the Blynk application. This setup enables real-time data visualization on a customized Blynk dashboard, ensuring continuous health and location monitoring and facilitating immediate responses in emergencies. This system significantly improves the situational awareness and operational readiness of soldiers.
Components Required
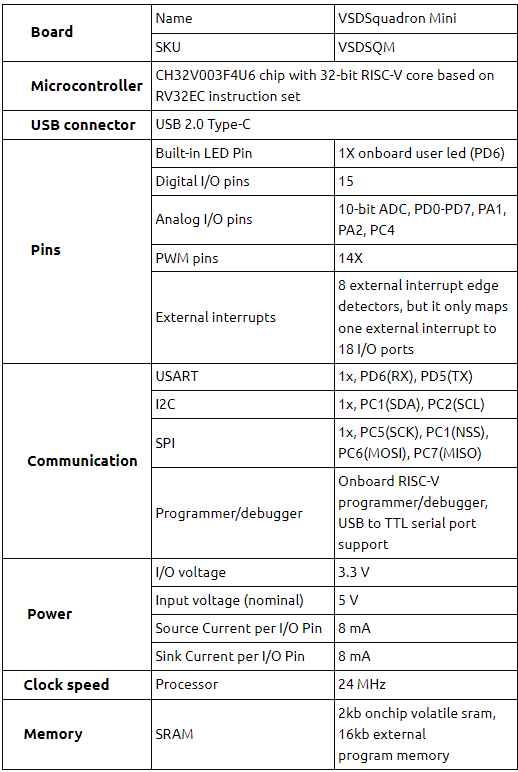
- VSD Squadron Mini developement board with CH32V003F4U6 chip with 32-bit RISC-V core based on RV32EC instruction set
- RC-A-4015 Pulse Sensor
- Neo-6M GPS Receiver
- Bread Board
- Jumper Wires
Software Required
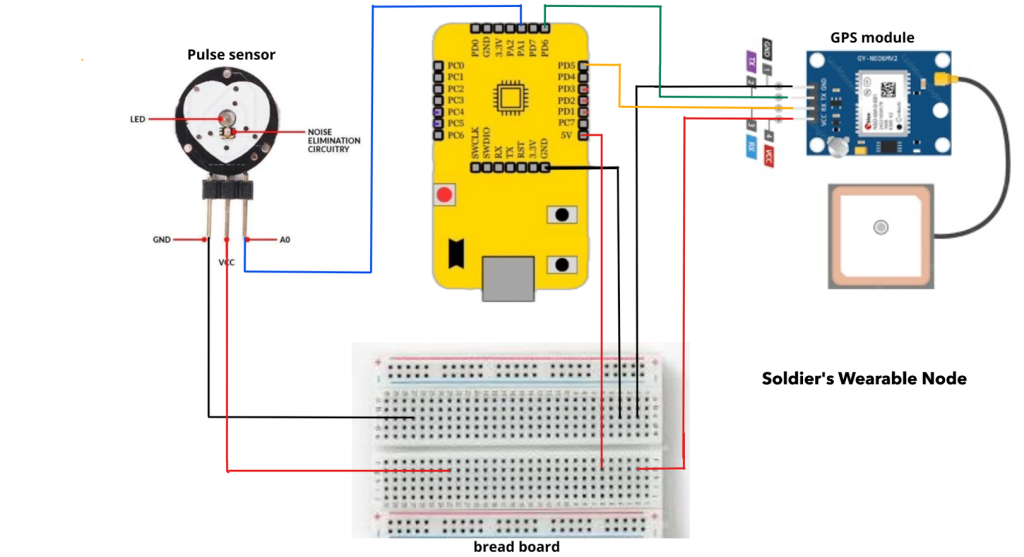
Circuit Connection Diagram

Table for Pin Connection
| RC-A-4015 Pulse Sensor | VSD Squadron Mini |
|---|---|
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 5V |
| A0 | PA1 |
| Neo-6M GPS Receiver | VSD Squadron Mini |
|---|---|
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 5V |
| TX | PD6 (RX) |
| RX | PD5 (TX) |
Demo
This is an example video:
Note: GPS module has stability issue to lock onto satellite, was not able to interface it with given time constraint, we are actively working on a fix
Advantages: Keeping in mind the ultimate goal of this hackathon, that is fault injection, we believe that this could see it’s applications in military wherein soldiers using such monitoring systems can keep the central unit updated about their positions and health vitals and in case of other countries’ intelligence agencies trying to interfere with such systems, our aim is to pentest it and find a viable solution to safeguard such systems and keep our defences non-vulnerable and safe.
Code
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#define PULSE_SENSOR_PIN A0
#define GPS_RX_PIN 3
#define GPS_TX_PIN 2
TinyGPSPlus gps;
SoftwareSerial gpsSerial(GPS_RX_PIN, GPS_TX_PIN); // RX, TX
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Pulse Sensor Reading:");
// Initialize GPS module
gpsSerial.begin(9600); // Change baud rate to match your GPS module
}
void loop() {
// Read pulse sensor value
uint16_t pulseValue = analogRead(PULSE_SENSOR_PIN);
// Print pulse sensor value to console
Serial.print("Pulse Sensor Value: ");
Serial.println(pulseValue);
// Read GPS data
while (gpsSerial.available() > 0) {
if (gps.encode(gpsSerial.read())) {
if (gps.location.isValid()) {
// Display GPS location
Serial.print("Latitude: ");
Serial.print(gps.location.lat(), 6);
Serial.print(", Longitude: ");
Serial.println(gps.location.lng(), 6);
}
}
}
// Delay for 1 second
delay(1000);
}Team Members – Bipin Raj C , B Jnyanadeep
College – RV College of Engineering